-
Document
-
Data Release
-
Update
-
Statistics
Document
1.Brief introduction
Synonymous substitution (which is often called silent mutation before) is a kind of point mutation occurs in genes' coding region.
Because the codons' degeneracy, it does not alter the Amino acid residue. As a result, for a long time, it's considered no bio function, treated as "silent".
But recent research shows "Silent Mutation Make Some Noise", and makes people focus on the area. Efforts have been made, one possible mechanism has been proposed, and synonymous mutations specifically change the splicing motifs and cause abnormal splicing.
However, there is no database focusing on the dangerous of synonymous mutations yet. Therefore, we have collected diseases related mutation to construct a Database of Deleterious Synonymous mutation (dbDSM) that would help in understanding the relationship between diseases and the synonymous mutations. Here we present the updated dbDSMv2.0 database, which newly added the tmVar data and updated ClinVar, GWAS Catalog data. In the new version of the database, we added new annotation features, including transcripts, conservatism, etc and we used the voting method to integrate the scores of the five scoring tools (SilVA, DDIG-SN, FATHMM-MKL, CADD, and TraP) which is named dbDSMScore to further assess the deleterious of the variants. Notably, variants from the original literature are marked in red.
But recent research shows "Silent Mutation Make Some Noise", and makes people focus on the area. Efforts have been made, one possible mechanism has been proposed, and synonymous mutations specifically change the splicing motifs and cause abnormal splicing.
However, there is no database focusing on the dangerous of synonymous mutations yet. Therefore, we have collected diseases related mutation to construct a Database of Deleterious Synonymous mutation (dbDSM) that would help in understanding the relationship between diseases and the synonymous mutations. Here we present the updated dbDSMv2.0 database, which newly added the tmVar data and updated ClinVar, GWAS Catalog data. In the new version of the database, we added new annotation features, including transcripts, conservatism, etc and we used the voting method to integrate the scores of the five scoring tools (SilVA, DDIG-SN, FATHMM-MKL, CADD, and TraP) which is named dbDSMScore to further assess the deleterious of the variants. Notably, variants from the original literature are marked in red.
2.The sources of the data
| Data source | dbDSMv1.0 | dbDSMv2.0 |
|---|---|---|
| 1.Manually curated | Yes | Yes |
| 2.GRASP | Yes | Yes |
| 3.ClinVar | Yes | Yes |
| 4.PolymiRTS | Yes | Yes |
| 5.GWAS catalog | Yes | Yes |
| 6.GWASdb | Yes | Yes |
| 7.tmVar | No | Yes |
3.The sum of the data
| SNPs | Number of records in dbDSMv1.0 | Number of records in dbDSMv2.0 |
|---|---|---|
| With ref ID | 1219 | 2116 |
| Without ref ID | 116 | 631 |
| Total | 1335 | 2747 |
4.The DSMs classification

To the best of our knowledge, there is no consensus classification of molecular mechanisms by which synonymous mutations contribute to disease phenotype.
Therefore, after reviewing the literature (Bali and Bebok, 2015; Gotea et al, 2015; Hunt et al, 2014; Sauna and Kimchi-Sarfaty, 2011),
we used a classification system in the database as follows:
| Classification | Description |
|---|---|
| Splicing regulation | Synonymous mutations may disrupt critical elements necessary for splicing, which could result in multiple outcomes, such as exon truncation, exon skipping, and intron inclusion. |
| mRNA structure | Synonymous mutations can alter mRNA structure, which in turn can change transcript stability and translation dynamics. |
| microRNA binding | Synonymous mutations can change the nucleotide sequence recognized by microRNAs, which can alter gene expression levels. |
| Transcription factor regulation | Synonymous mutations can add or subtract exonic transcription factor binding sites, leading to altered gene expression levels. |
| Protein synthesis | Protein translation and folding can also be influenced by synonymous mutations through codon usage (rare versus frequent codons), tRNA availability, mRNA shape, and ribosome structure. |
| n/a | If the mechanism is not available, the classification information is indicated as n/a. |
References:
Bali, V., & Bebok, Z. (2015). Decoding mechanisms by which silent codon changes influence protein biogenesis and function. The International Journal of Biochemistry & Cell Biology, 64, 58-74.
Gotea, V., Gartner, J. J., Qutob, N., Elnitski, L., & Samuels, Y. (2015). The functional relevance of somatic synonymous mutations in melanoma and other cancers. Pigment Cell & Melanoma Research, 28(6), 673-684.
Hunt, R. C., Simhadri, V. L., Iandoli, M., Sauna, Z. E., & Kimchi-Sarfaty, C. (2014). Exposing synonymous mutations. Trends in Genetics, 30(7), 308-321.
Sauna, Z. E., & Kimchi-Sarfaty, C. (2011). Understanding the contribution of synonymous mutations to human disease. Nature Reviews Genetics, 12(10), 683-691.
5.Strength of evidence for variant assessment
| Evidence leading to a pathogenic assertion | Strength of evidence |
|---|---|
| Significant segregation in affected family members (LOD >2) | 3 |
| Confirmed de novo inheritance in relevant disease-associated gene | 3 |
| In vivo data from mammalian model organisms suggest an impact on function | 2 |
| Case-control studies significantly associate the variant to disease | 2 |
| Nucleotide and amino acid strongly conserved in distantly related species | 2 |
| In vitro data from recombinant DNA constructs or proteins suggest an impact on function | 1 |
| Variant is present in trans with an established pathogenic variant in recessive disease | 1 |
| Variant is rare or absent in large population studies | 1 |
| Computational tools predict an impact on function and/or splicing | 1 |
References:
Duzkale, H., Shen, J., McLaughlin, H., Alfares, A., Kelly, M. A., Pugh, T. J., ... & Lebo, M. S. (2013). A systematic approach to assessing the clinical significance of genetic variants. Clinical genetics, 84(5), 453-463.
6. The annotation tools used in dbDSMv2.0
| Tool | Genomic build | Source | Threshold | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SilVA | GRCh37/hg19 | http://compbio.cs.toronto.edu/silva | >0.278 | [1] |
| DDIG-SN | GRCh37/hg19 | http://sparks-lab.org/ddig | >0.5 | [2] |
| FATHMM-MKL | GRCh37/hg19 | http://fathmm.biocompute.org.uk | >0.5 | [3] |
| TraP | GRCh37/hg19 | http://trap-score.org/Search?version=v2 | ≧0.459 | [4] |
| CADD | GRCh37/hg19 | https://myvariant.info | 10-20 | [5] |
| GERP++ | GRCh37/hg19 | https://myvariant.info | >0 | [5] |
| Phylop100way | GRCh38/37 | http://genome.ucsc.edu/cgi-bin/hgTables | >0 | [6] |
| PhastCons100way | GRCh38/37 | http://genome.ucsc.edu/cgi-bin/hgTables | >0.5 | [6] |
| TransVar | GRCh38/37 | http://bioinformatics.mdanderson.org/transvarweb/ | - | [7] |
| VEP | GRCh38/37 | http://www.ensembl.org/Tools/VEP | - | [8] |
References:
[1] Buske, O. J., Manickaraj, A., Mital, S., Ray, P. N., & Brudno, M. (2013). Identification of deleterious synonymous variants in human genomes. Bioinformatics, 29(15), 1843-1850.
[2] Livingstone, M., Folkman, L., Yang, Y., Zhang, P., Mort, M., Cooper, D. N., ... & Zhou, Y. (2017). Investigating DNA‐, RNA‐, and protein‐based features as a means to discriminate pathogenic synonymous variants. Human mutation, 38(10), 1336-1347.
[3] Shihab, H. A., Rogers, M. F., Gough, J., Mort, M., Cooper, D. N., Day, I. N., ... & Campbell, C. (2015). An integrative approach to predicting the functional effects of non-coding and coding sequence variation. Bioinformatics, 31(10), 1536-1543.
[4] Gelfman, S., Wang, Q., McSweeney, K. M., Ren, Z., La Carpia, F., Halvorsen, M., ... & Petrovski, S. (2017). Annotating pathogenic non-coding variants in genic regions. Nature communications, 8(1), 236.
[5] Xin, J., Mark, A., Afrasiabi, C., Tsueng, G., Juchler, M., Gopal, N., ... & Torkamani, A. (2016). High-performance web services for querying gene and variant annotation. Genome biology, 17(1), 91.
[6] http://genome.ucsc.edu/cgi-bin/hgTables
[7] Zhou, W., Chen, T., Chong, Z., Rohrdanz, M. A., Melott, J. M., Wakefield, C., ... & Chen, K. (2015). TransVar: a multilevel variant annotator for precision genomics. Nature methods, 12(11), 1002.
[8] McLaren, W., Gil, L., Hunt, S. E., Riat, H. S., Ritchie, G. R., Thormann, A., ... & Cunningham, F. (2016). The ensembl variant effect predictor. Genome biology, 17(1), 122.
7.The overview of the searching process
The browse process including “Search” and “Advanced search”.
1)Search
You can input one keyword to search the dbDSM. The search fields include disease name, gene name, GRCh38 genome position, deleterious synonymous mutation (c.DNA, protein, rsid).
1)Search
You can input one keyword to search the dbDSM. The search fields include disease name, gene name, GRCh38 genome position, deleterious synonymous mutation (c.DNA, protein, rsid).
2) Advanced search
You can select one or more of the four options listed in the browse area (Gene, Disease, dbDSMScore, Chromosome).
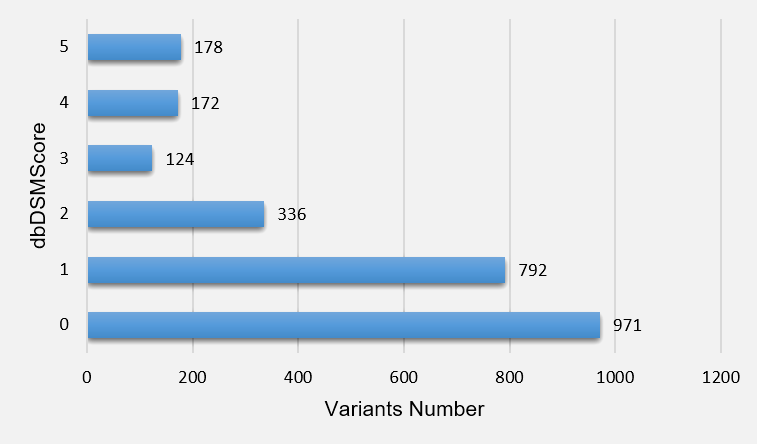
8.Statistics dbDSMScore
Data Release
Data release of dbDSM v2
| ClinVar | Description | Public archive of interpretations of clinically relevant variants |
| Download | ftp://ftp.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pub/clinvar/tab_delimited/ | |
| Release | 2018/07/09 | |
| GRASP | Description | Genome-Wide Repository of Associations Between SNPs and Phenotypes |
| Download | https://s3.amazonaws.com/NHLBI_Public/GRASP/GraspFullDataset2.zip | |
| Release | GRASP 2.0.0.0 | |
| GWAS Catalog | Description | The NHGRI-EBI Catalog of published genome-wide association studies |
| Download | http://www.ebi.ac.uk/gwas/downloads | |
| Release | v1.0.2 _e92_r2018/06/25 | |
| PolymiRTS 3.0 | Description | Polymorphism in microRNAs and their TargetSites |
| Download | http://compbio.uthsc.edu/miRSNP/download/ | |
| Release | PolymiRTS3.0_2013/07/22 | |
| GWASdb | Description | A database for human genetic variants identified by genome-wide association studies |
| Download | http://jjwanglab.org/gwasdb | |
| Release | 2015/08 | |
| Manually curated | Description | An extensive literature query of PubMed database and Web of Knowledge using a list of keywords |
| Download | PubMed database and Web of Knowledge | |
| Release | 2015/12/31 | |
| tmVar | Description | tmVar extracts a wide range of sequence variants in both protein and gene levels (e.g. substitution, deletion, etc) in HGVS formats |
| Download | ftp://ftp.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pub/lu/PubTator/ | |
| Release | 2017/12/09 |
Update
Brief release history
07/06/2019: The Database of Deleterious Synonymous Mutation Version 2 (dbDSM v2) is updating.
08/31/2018: Data from tmVar added and ClinVar,GWAS Catalog updated.
09/21/2017: Manually curated data from PubMed and Web of Knowledge updated.
01/21/2016: Nearly one hundred entries were updated into dbDSM.
01/18/2016: Download page updated.
01/17/2016: Data in dbDSM were updated based on the comments from anonymous reviewers.
11/17/2015: Data from GRASdb added.
11/11/2015: Home page updated.
10/15/2015: Document page updated.
10/07/2015: Submit page updated.
09/20/2015: Release the dbDSM.
08/31/2018: Data from tmVar added and ClinVar,GWAS Catalog updated.
09/21/2017: Manually curated data from PubMed and Web of Knowledge updated.
01/21/2016: Nearly one hundred entries were updated into dbDSM.
01/18/2016: Download page updated.
01/17/2016: Data in dbDSM were updated based on the comments from anonymous reviewers.
11/17/2015: Data from GRASdb added.
11/11/2015: Home page updated.
10/15/2015: Document page updated.
10/07/2015: Submit page updated.
09/20/2015: Release the dbDSM.
Statistics
Fields statistics
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| dbDSMAccNum | The access number of a variant in dbDSM |
| Gene | Gene name |
| GeneID | The unique identifier for a gene |
| MIM | The identifier of a gene linked to OMIM database |
| Map_Location | The map location for this gene |
| VariantType | Germline or somatic mutation |
| Disease | The main phenotype of the patient |
| DOID | The identifier of a disease linked to OMIM database |
| SNPID | dbSNP identifier of the variant. If there is no rs id this field is “n/a“ |
| GRCh38_Position | Genomic position in GRCh38 |
| GRCh37_Position | Genomic position in GRCh37 |
| Ref | Reference allele |
| Alt | Alternate allele |
| Strand | A variant occurred in forword chain(+) or reverse chain(-) |
| c.DNA | A coding reference level representation of the variant |
| Protein | A protein reference level representation of the variant |
| CodonChange | Reference codon > Alternate codon |
| RefseqTranscript | Refseq Transcript that the variant resides on |
| P_Value | P-value in GWAS |
| PhyloP100way | 100 Vertebrate Phylop conservation score at mutation position |
| PhastCons100way | 100 Vertebrate PhastCons conservation score at mutation position |
| GerpS | Rejected Substitution' score defined by GERP++ |
| Source | The source of a variant |
| dbDSMScore | dbDSM score of a variant Which are including SilVA,DDIG-SN,FATHMM-MKL, TraP, CADD score.We use voting methods to evaluate the variant, dbDSM score plus one if the score above the threshold value for each tool. |
| PMID | Pubmed ID for an article |
| Year | Published time of an article |
| KeySentence | Deleterious evidence of a variant extracted from the article |
| Classification | Deleterious mechanism of a variant |
| StrengthOfEvidence | Clinical classification of a variant |
Data statistics
| Entries | Disease | 1499 |
| Gene | 1624 | |
| Variants | 2747 | |
| Chromosomal location | Variants Entries mapped to chromosome 1 | 258 |
| Variants Entries mapped to chromosome 2 | 163 | |
| Variants Entries mapped to chromosome 3 | 136 | |
| Variants Entries mapped to chromosome 4 | 90 | |
| Variants Entries mapped to chromosome 5 | 95 | |
| Variants Entries mapped to chromosome 6 | 216 | |
| Variants Entries mapped to chromosome 7 | 119 | |
| Variants Entries mapped to chromosome 8 | 67 | |
| Variants Entries mapped to chromosome 9 | 92 | |
| Variants Entries mapped to chromosome 10 | 99 | |
| Variants Entries mapped to chromosome 11 | 183 | |
| Variants Entries mapped to chromosome 12 | 133 | |
| Variants Entries mapped to chromosome 13 | 64 | |
| Variants Entries mapped to chromosome 14 | 50 | |
| Variants Entries mapped to chromosome 15 | 102 | |
| Variants Entries mapped to chromosome 16 | 134 | |
| Variants Entries mapped to chromosome 17 | 178 | |
| Variants Entries mapped to chromosome 18 | 26 | |
| Variants Entries mapped to chromosome 19 | 137 | |
| Variants Entries mapped to chromosome 20 | 46 | |
| Variants Entries mapped to chromosome 21 | 26 | |
| Variants Entries mapped to chromosome 22 | 49 | |
| Variants Entries mapped to chromosome X | 109 | |
| Variants Entries mapped to chromosome Y | 0 | |
| Variants Entries mapped to chromosome MT | 1 | |
| Publications | tmVar publications | 2548 |
| ClinVar publications | 510 | |
| GRASP publications | 196 | |
| GWASdb publications | 357 | |
| PolymiRTS publications | 80 | |
| GWAS Catalog publications | 179 | |
| Manual Read publications | 195 |